Kidney stones, also referred to as renal calculi, are solid formations composed of crystals. They originate within the kidneys & can potentially form within the urinary tract. Renowned for their excruciating nature, kidney stones are widely regarded as one of the most agonizing medical ailments.
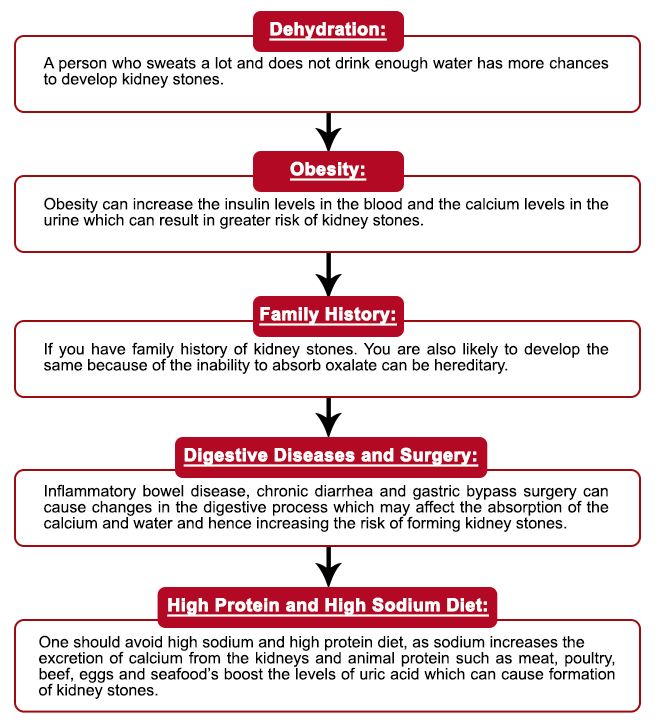
SYMPTOMS OF KIDNEY STONE:
- Urinating small amounts or more frequently than usual.
- Sudden & severe abdominal pain.
- Nausea & vomiting.
- Pain during urination.
- Presence of blood in the urine.
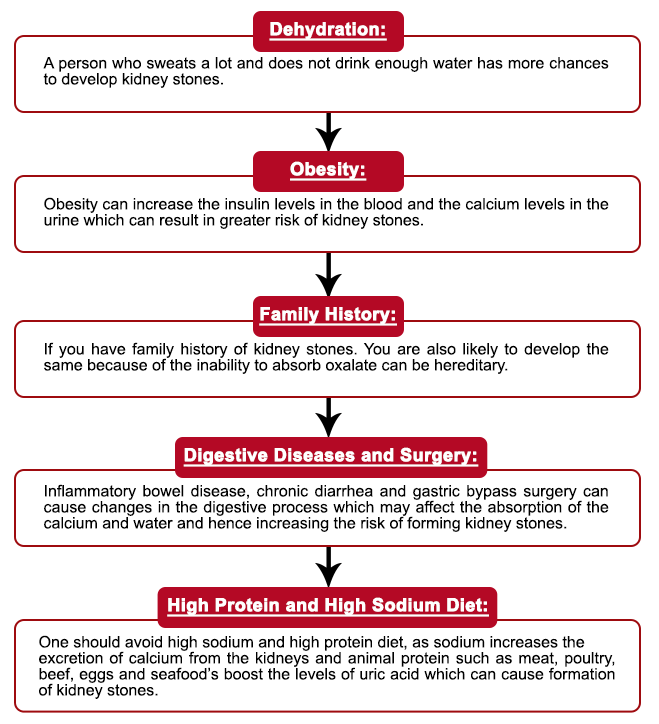
Causes of Kidney Stones
Here are the possible causes of Kidney Stones:
- Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake can lead to concentrated urine, increasing the risk of kidney stone formation.
- Dietary Factors: Consuming a diet high in sodium, oxalate, or animal protein can contribute to the development of kidney stones.
- Family or Personal History: Having a family history of kidney stones or having experienced them in the past increases the likelihood of developing them again.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Conditions such as urinary tract infections, kidney diseases, & metabolic disorders can make a person more prone to kidney stone formation.
- Certain Medications: Some medications, such as diuretics & certain antiretroviral drugs, can increase the risk of kidney stone formation.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of kidney stone development.
- Inadequate Fluid Intake: Not drinking enough water or fluids can contribute to the formation of kidney stones.
- Urinary Tract Blockage: Blockages or obstructions in the urinary tract, such as from kidney or bladder abnormalities, can lead to the formation of kidney stones.
- Climate or Occupation: Living in hot climates or working in occupations that involve prolonged exposure to heat & dehydration can increase the risk of kidney stones.
- Other Factors: Certain lifestyle factors, such as a sedentary lifestyle or excessive intake of certain supplements (e.g., vitamin D or calcium), may also play a role in kidney stone formation.
Dietary guidelines
Let us look at foods to avoid in the diet:
- VITAMIN C: Vitamin C may convert stones to oxalates, potentially worsening the problem.
- SODIUM INTAKE: Patients with kidney stones, especially calcium stones, should restrict their sodium intake.
- PROTEIN INTAKE: Protein can increase uric acid, calcium, & oxalates in the urine while reducing citrate. High-protein diets, particularly those rich in meat protein, have been consistently linked to kidney stones. Foods such as soybeans, mushrooms, eggs, spinach, asparagus, cauliflower, red meats, poultry, & fish should be avoided.
| FOOD GROUPS | CHOOSE THESE | NOT THESE |
|---|---|---|
|
CEREALS |
|
|
|
PULSES |
|
|
|
VEGETABLES |
|
|
|
FRUITS |
|
|
|
NON-VEGETARIAN
|
|
|
|
MILK & MILK PRODUCTS |
|
|
|
NUTS |
|
|
|
SUGARS |
|
|
|
MISCELLANEOUS FOOD ITEMS |
|
|
|
NON-ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES |
|
|
|
SUPPLEMENTS |
|
|
| Type Of Stones | Uric Acid Stones | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Food groups |
Choose freely |
Choose moderately |
Choose rarely |
|
Cereals |
|
- |
- |
|
Pulses & dal |
|
|
- |
|
Milk & milk products |
|
|
|
|
Non-veg |
|
|
|
|
Fruits |
|
- |
- |
|
Nuts |
|
- |
|
|
Vegetables |
|
|
- |
MAKE YOUR KIDNEYS STONE PROOF!